×
Table of Contents
About Promise
How Promises Work
A promise is an object which can be returned synchronously from an asynchronous function.
It will be in one of 3 possible states:
- Fulfilled: onFulfilled() will be called (e.g., resolve() was called)
- Rejected: onRejected() will be called (e.g., reject() was called)
- Pending: not yet fulfilled or rejected
Promises following the spec must follow a specific set of rules:
- A promise or “thenable” is an object that supplies a standard-compliant .then() method.
- A pending promise may transition into a fulfilled or rejected state.
- A fulfilled or rejected promise is settled, and must not transition into any other state.
- Once a promise is settled, it must have a value (which may be undefined). That value must not change.
- A Promise can be resolved or rejected, exclusively and only once.
- A call to promise.then returns a promise, so that we can call the next promise
- A value returned by a .then handler is immediately passed to the next handler
- If the returned value is a promise, then the further execution is suspended until it settles.
- A fetch() promise will reject with a TypeError when a network error is encountered or CORS is misconfigured on the server side
- By default, fetch won’t send or receive any cookies from the server
Chained Promises
Chained Promises Sample
function testMe(myUrl, test, dataError) {
dumpMessage("Testing Promise Chaining: " + test, false);
let url = myUrl;
fetch(url) // fetch returns a promise
.then(response => { // Our Success Handler returns response Object
if(response.ok) {
if ( dataError) { // Just for testing - Mimicking a Data Proessing Error
throw new Error('Data Processing Error');
}
return response.json();
}
throw new Error('Network response was not ok at Chain Level 1');
}) // Catches Exception for our Success Handler and for our Reject Handler
.catch(e => {
dumpMessage("Exception at Chain Level 1 : " + e,true );
throw new Error('Initial Fetch failed for URL: ' + url);
})
.then(jsonData => { dumpMessage("ID: " + jsonData.id + " - name : " + jsonData.name,false ); return(jsonData.name);} )
.then( (user) => { dumpMessage("Username: " + user, false); return fetch("https://api.github.com/users/"+user ); })
// Load the response as json
.then(response => response.json())
// Show the avatar image (githubUser.avatar_url) for 3 seconds (maybe animate it)
.then(githubUser => {
dumpMessage("Displaying Github Avatar Image for 3 seconds!", false);
let img = document.createElement('img');
img.src = githubUser.avatar_url;
img.className = "promise-avatar-example";
document.body.append(img);
setTimeout(() => {
img.remove();
dumpMessage("Removed Github Avatar Image !", false);
}, 3000); // (*)
})
.catch(err => { // Catch all Hanlder return true/false for retry logic
dumpMessage("CatchAll Error-handler: " + err, true);
});
}
Promises and Error Handling
Overview
| Pomisess Error Handling Diagram |
|---|
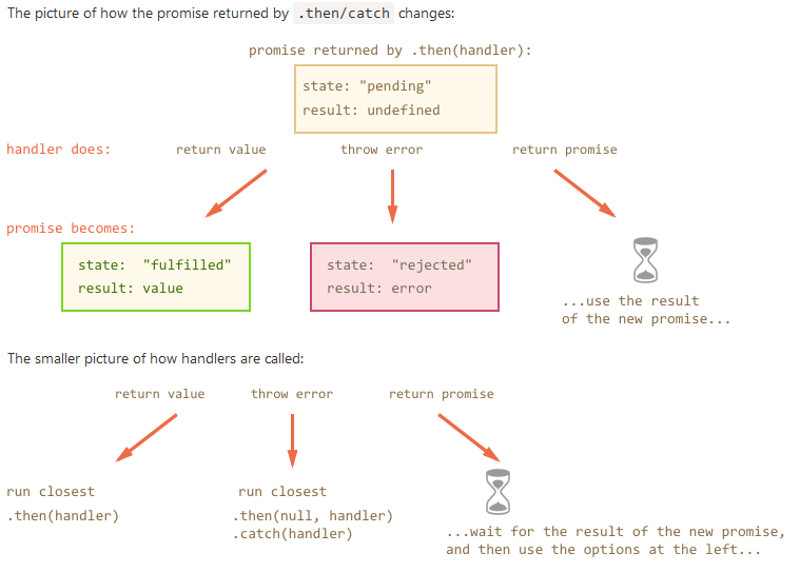 |
Handle Errors – Pattern 1
save().then(
handleSuccess,
handleError
);
- Problem Exceptions in handleSuccess() are not catched
Handle Errors – Pattern 2
save()
.then(handleSuccess)
.catch(handleError)
Sample:
fetch(url) // fetch returns a promise
.then(response => { // Our Success Handler returns response Object
if(response.ok) {
if ( dataError) { // Just for testing - Mimicking a Data Proessing Error
throw new Error('Data Processing Error');
}
return response.json();
}
throw new Error('Network response was not ok at Chain Level 1');
}) // Catches Exception for our Success Handler and for our Reject Handler
.catch(e => {
dumpMessage("Exception at Chain Level 1 : " + e,true );
throw new Error('Initial Fetch failed for URL: ' + url);
})
.then(jsonData => { dumpMessage("ID: " + jsonData.id + " - name : " + jsonData.name,false ); return(jsonData.name);} )
...
- Handles both Processing Errors and Network Errors
- CodePen Project: Press Invalid URL & Data Error Button
Handle Errors – Pattern 3
save()
.then(
handleSuccess,
handleNetworkError -> Handle and Fix Network Error
)
.catch(handleProgrammerError) -> Handle anf Fix ProgamError in handleSucessFunction
Sample:
fetch(url)
.then(response => { // Our Success Handler
if(response.ok) {
if ( dataError) { // Mimicking a Data Proessing Error
throw new Error('Data Processing Error');
}
return response.json();
}
throw new Error('Network response was not ok.');
},
err => { // Now we handle the error (rejection reason)
dumpMessage("Handle error (rejection reason): " + err,true );
// Create a Dummy object
dumpMessage("Create a Default Object to Finish Promise Chain");
myObj = { "name":"hhutzler", "id":999 };
return myObj;
} )
.catch(e => { dumpMessage("Processing Error Chaining at Level 1 : " + e,true );
dumpMessage("Create a Default Object to Finish Promise Chain");
myObj = { "name":"hhutzler", "id":999 };
return myObj;
})
// , // Now we handle the error (rejection reason)
//e => { dumpMessage("Initial Fetch Error: " + e,true ); throw new Error('Initial Fetch Error for URL' + url); } )
//.then(response => response.json() )
.then(jsonData => { dumpMessage("ID: " + jsonData.id + " - name : " + jsonData.name,false ); return(jsonData.name);} )
....
- Allows us to handle Network errors and Program Errors individually
- CodePen Project: Press FIX Invalid URL & FIX Data Error Button